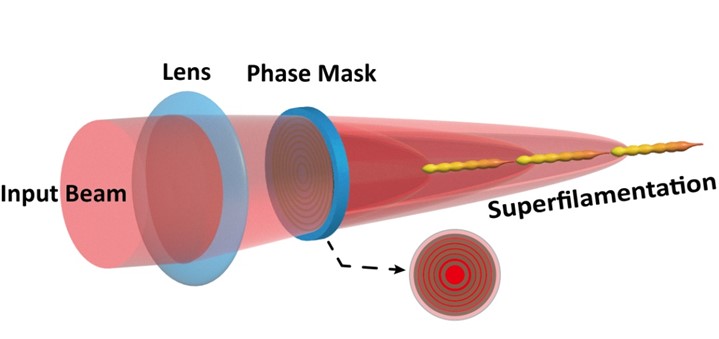
Extending filamentation guided discharges using a multifocus phase mask
Laser filamentation is a nonlinear optical phenomenon that can be obtained using intense ultrashort lasers. It allows the formation in the atmosphere of long ionizing light strings that can be used for different applications such as the channeling of optical, microwave or electrical energy by the filament plasma strings. The most spectacular application of these laser filaments is the recent demonstration of laser guided lightning published in 2023 (A. Houard et al. Nature Phot. 17, 231 (2023)) by the F-ILM group.
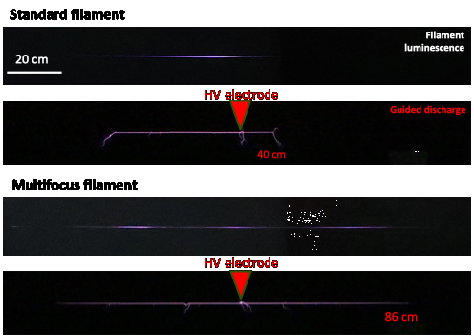
A strong limitation in the current techniques used to produce long and dense filaments is that the laser energy is not efficiently used to produce plasma over a long distance, limiting the scalability of the filament. In a new publication, researchers of LOA’s F-ILM group now demonstrate an extension of the superfilamentation length of a focused terawatt laser beam using a specially designed multifocal phase mask. They also demonstrate in the laboratory the ability of these extended filaments to guide electric discharges and optical signals over distances 2 or 3 times longer than a classical filament.
This multi-focus method has the potential to extend the range of numerous atmospheric applications of laser filaments, such as the laser lightning rod, and optical communication through clouds, where a very long superfilamentation regime is required.
Also available on the French open access repository HAL.